17 May 2024, 17:56
中国国家儿童医学中心、复旦大学附属儿科医院的医学研究团队开发出一种不损伤脑组织的冷冻和解冻技术。
在发表于《细胞报告方法》杂志的研究中,研究小组测试了将脑类器官浸泡在各种化合物中,然后用液氮冷冻的效果。
先前的研究表明,无论脑组织冷冻速度有多快,冻融过程总会造成组织损伤。这给研究人员的工作带来了更多挑战,因为研究必须在获取组织样本后立即进行。在这项新研究中,中国团队找到了一种解决这个问题的方法,即在冷冻前将组织浸泡在一种特殊的溶液中。
这项研究包括将脑类器官(由干细胞培养的脑组织)浸泡在各种化合物中,然后进行冷冻和解冻,以评估组织的健康状况。经过多次尝试,他们找到了一种效果最佳的溶液组合——乙二醇、甲基纤维素DMSO和Y27632的混合物。他们将这种混合物命名为MEDY。
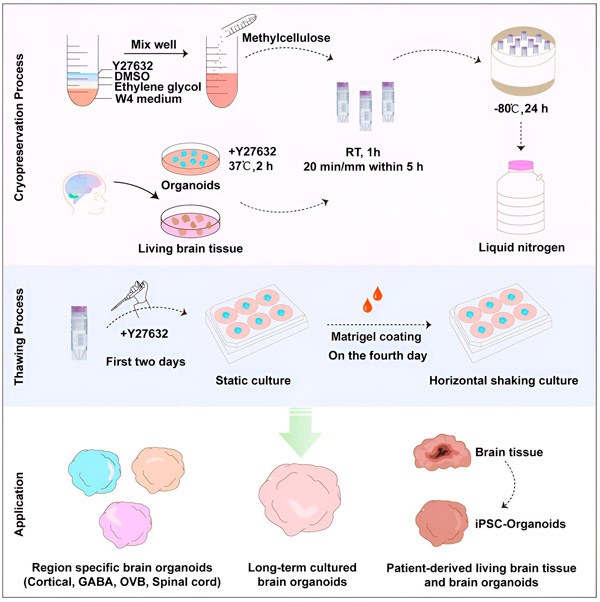
研究团队随后在各种条件下测试了MEDY,以评估其防止冻害的效果。测试条件包括改变类器官冷冻前的年龄以及在MEDY溶液中浸泡的时间等变量。之后,他们让类器官在解冻后继续生长,最长可达150天。
研究人员发现,冷冻的类器官和未冷冻的类器官之间几乎没有区别,即使冷冻时间长达 18 个月。
作为最后的测试,研究小组将他们的技术应用于从活体患者身上采集的脑组织样本,发现效果同样良好。
研究小组表示,他们的技术应该可以让研究人员存储足够大规模的脑组织样本,从而开展对大脑和神经系统的新型研究。

