
15 May 2024, 19:05
根据发表在《PNAS Nexus》杂志上的一项研究,服用益生元和益生菌可能会使人们对公平更加敏感,即使以损失金钱为代价。
人类肠道微生物群在塑造行为中的作用才刚刚开始被探索。Hilke Plassmann 及其同事测试了服用益生元和益生元是否会影响利他惩罚的程度。
51 名参与者服用含有乳酸杆菌和双歧杆菌的补充剂,持续七周。另外 50 名参与者作为对照组,服用安慰剂。
在补充治疗七周前后,参与者被要求玩一场“最后通牒游戏”。游戏中,一位玩家控制一笔钱,可以提出分享,也可以与另一位玩家“分割”。另一位玩家可以接受提议并拿走这笔钱,也可以拒绝,在这种情况下,两位玩家都不会得到钱。拒绝不公平的提议被解读为“利他惩罚”,因为拒绝者会牺牲任何小额的份额,以惩罚第一位玩家的不够慷慨。
服用补充剂的玩家更有可能拒绝报价。尤其是,他们更有可能拒绝分成比例为 30% 到 40% 的报价。(所有玩家都倾向于拒绝分成比例极不均等的报价。)
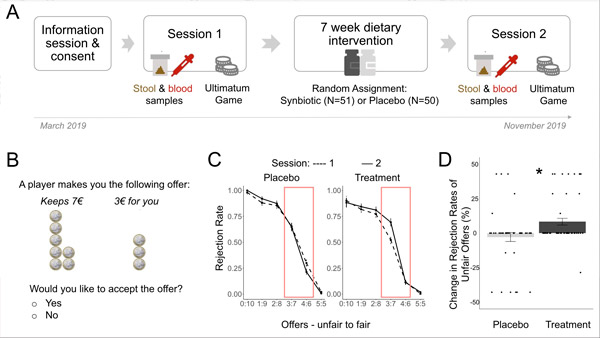
(A)研究流程和随机化。(B)最后通牒博弈中不公平提议的示例。(C)各组和各环节所有提议的拒绝率分布。(D)各组各环节中不公平提议的拒绝率变化(为便于查看,点略有移动)。来源:Plassmann 等人。
研究开始时厚壁菌门与拟杆菌门比例较高的玩家,其肠道菌群组成和利他惩罚水平的变化最为显著。在一些参与者中,补充剂降低了血浆中多巴胺前体酪氨酸的水平,而这些玩家的利他惩罚水平也出现了最大幅度的提升。
据作者称,将肠道微生物群改变到更健康状态的人变得不那么理性,对社会方面更加敏感。

