
17 May 2024, 19:51
跑步机训练是一种耐力训练,研究发现其非常有效,“只需[一到两周]就能显著提高骨骼肌柠檬酸合酶活性,四到八周后就能提高最大跑步速度和最大摄氧量”。在这项研究之前,尚未有人对耐力训练的全部效果进行过解释。
研究人员的目标是制定并实施一套标准化的耐力训练方案,该方案涉及 340 多只老鼠,每周五天进行为期一、二、四或八周的渐进式跑步机训练。
研究人员收集并测量了18个组织、血液和血浆样本,以确定耐力训练的效果。接受耐力训练的大鼠骨骼肌柠檬酸合酶活性(线粒体密度的标志)的提高至关重要,因为它能为工作肌肉提供更多能量,使它们能够工作更长时间、更快。
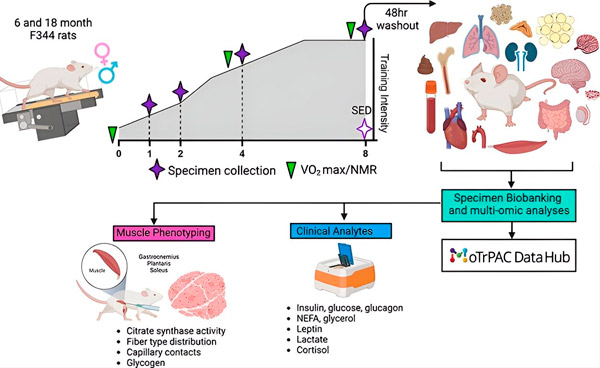
文章“成年和老年大鼠对渐进式耐力训练的生理适应:来自分子传感器体力活动联盟(MoTrPAC)的见解”发表在《Function》杂志上。
研究人员写道:“这项针对成熟跑步机训练大鼠的研究代表了研究临床前大鼠模型中耐力训练的时间、性别和年龄相关反应的最全面和前所未有的资源。”

